Auschwitz concentration camp
| Auschwitz | |
|---|---|
| Concentration camp | |
The main entrance to extermination camp Auschwitz-Birkenau |
|
 Location of Auschwitz in Poland
|
|
| Coordinates | |
| Location | Oświęcim, Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany |
| Operated by | the German Schutzstaffel (SS), the NKVD (after WWII) |
| Original use | Army barracks |
| Operational | May 1940–January 1945 |
| Inmates | mainly Jews, Poles, Roma, Soviet soldiers |
| Killed | 1.1 million (estimated) |
| Liberated by | Soviet Union, January 27, 1945 |
| Notable inmates | Viktor Frankl, Primo Levi, Witold Pilecki, Rudolf Vrba, Elie Wiesel, Maximillian Kolbe |
| Notable books | If This is a Man, Night, Man's Search for Meaning |
| Website | Auschwitz-Birkenau State Museum |
Auschwitz (German pronunciation: [ˈaʊʃvɪts]; Konzentrationslager Auschwitz) was a network of concentration and extermination camps built and operated in Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany during the Second World War. It was the largest of the German concentration camps, consisting of Auschwitz I (the Stammlager or base camp); Auschwitz II-Birkenau (the Vernichtungslager or extermination camp); Auschwitz III-Monowitz, also known as Buna-Monowitz (a labor camp); and 45 satellite camps.[1]
Auschwitz is the German name for Oświęcim, the town in and around which the camps were located; it was renamed by the Germans after they invaded Poland in September 1939. Birkenau, the German translation of Brzezinka (birch tree), refers to a small Polish village nearby that was mostly destroyed by the Germans to make way for the camp.
Auschwitz II-Birkenau was designated by Heinrich Himmler, who was the Reichsführer and Germany's Minister of the Interior, as the locus of the "final solution of the Jewish question in Europe". From spring 1942 until the fall of 1944, transport trains delivered Jews to the camp's gas chambers from all over Nazi-occupied Europe.[2] The camp's first commandant, Rudolf Höss, testified after the war at the Nuremberg Trials that up to three million people had died there (2.5 million exterminated, and 500,000 from disease and starvation),[3] a figure since revised to 1.1 million, around 90 percent of them Jews.[4] Others deported to Auschwitz included 150,000 Poles, 23,000 Roma and Sinti, 15,000 Soviet prisoners of war, and tens of thousands of people of diverse nationalities.[5] Those not killed in the gas chambers died of starvation, forced labor, lack of disease control, individual executions, and medical experiments.[6] Denis Avey, recently named a British Holocaust hero by the government of Britain, had escaped and spoke of conditions inside the camps.[7]
On January 27, 1945, Auschwitz was liberated by Soviet troops, a day commemorated around the world as International Holocaust Remembrance Day. In 1947, Poland founded a museum on the site of Auschwitz I and II, which by 1994 had seen 22 million visitors—700,000 annually—pass through the iron gates crowned with the infamous motto, Arbeit macht frei ("work makes you free").
Contents |
Camps
Main camps

The Auschwitz complex of camps encompassed a large industrial area rich in natural resources. There were 48 camps in all. The three main camps were Auschwitz I, Auschwitz II-Birkenau, and a work camp called Auschwitz III-Monowitz, or the Buna. Auschwitz I served as the administrative center, and was the site of the deaths of roughly 70,000 people, mostly ethnic Poles and Soviet prisoners of war. Auschwitz II was an extermination camp or Vernichtungslager, the site of the deaths of at least 960,000 Jews, 75,000 Poles, and some 19,000 Roma (Gypsies). Auschwitz III-Monowitz served as a labor camp for the Buna-Werke factory of the IG Farben concern. The SS-Totenkopfverbände (SS-TV) was the SS organization responsible for administering the Nazi concentration camps for the Third Reich. The SS-TV was an independent unit within the SS with its own ranks and command structure. Obersturmbannführer Rudolf Höss was overall commandant of the Auschwitz complex from May 1940–November 1943; Obersturmbannführer Arthur Liebehenschel from November 1943–May 1944; and Sturmbannführer Richard Baer from May 1944–January 1945.
Yisrael Gutman writes that it was in the concentration camps that Hitler's concept of absolute power came to fruition. Primo Levi, who described his year in Auschwitz in If This Is a Man, wrote:
[N]ever has there existed a state that was really "totalitarian." ... Never has some form of reaction, a corrective of the total tyranny, been lacking, not even in the Third Reich or Stalin's Soviet Union: in both cases, public opinion, the magistrature, the foreign press, the churches, the feeling for justice and humanity that ten or twenty years of tyranny were not enough to eradicate, have to a greater or lesser extent acted as a brake. Only in the Lager [camp] was the restraint from below non-existent, and the power of these small satraps absolute.[8]
Auschwitz I

Auschwitz I was the original camp, serving as the administrative center for the whole complex. The site for the camp—16 one-story buildings—had earlier served as Polish army artillery barracks. It was first suggested as a site for a concentration camp for Polish prisoners by SS-Oberfuhrer Arpad Wigand an aide to Higher SS and Police Leader for Silesia, Erich von dem Bach Zelewski. Bach Zeleski had been searching for a site to house prisoners in the Silesia region as the local prisons were filled to capacity. Richard Glucks head of the Concentration Camps Inspectorate sent former Sachsenhausen commandant, Walter Eisfeld to inspect the site. Glucks informed SS Reichsfuhrer Heinrich Himmler, that a camp would be built on the site on 21 February 1940.[9] Rudolf Höss would oversee the development of the camp and serve as the first commandant, SS-Obersturmführer Josef Kramer was appointed Höss's deputy.[10] Local residents were evicted, including 1,200 people who lived in shacks around the barracks, creating an empty area of 40 sq km, which the Germans called the "interest area of the camp." Three hundred Jewish residents of Oświęcim were brought in to lay foundations. The first prisoners—30 German criminal prisoners from the Sachsenhausen camp—arrived in May 1940, intended to act as functionaries within the prison system. The first transport of 728 Polish prisoners which included 20 Jews arrived on June 14, 1940 from the prison in Tarnow, Poland. They were interned in the former building of the Polish Tobacco Monopoly adjacent to the site, until the camp was ready. The inmate population grew quickly, as the camp absorbed Poland's intelligentsia and dissidents, including the Polish underground resistance. By March 1941, 10,900 were imprisoned there, most of them Poles.[10]
The SS selected some prisoners, often German criminals, as specially privileged supervisors of the other inmates (so-called: kapos). Although involved in numerous atrocities, only two were ever prosecuted for their individual behavior; many were deemed to have had little choice but to act as they did.[11] The various classes of prisoners were distinguishable by special marks on their clothes; Jews and Soviet prisoners of war were generally treated the worst. All inmates had to work in the associated arms factories, except on Sundays, which were reserved for cleaning and showering. The harsh work requirements, combined with poor nutrition and hygiene, led to high death rates among the prisoners.
Block 11 of Auschwitz was the "prison within the prison", where violators of the numerous rules were punished. Some prisoners were made to spend the nights in "standing cells". These cells were about 1.5 m2 (16 sq ft), and four men would be placed in them; they could do nothing but stand, and were forced during the day to work with the other prisoners. In the basement were located the "starvation cells"; prisoners incarcerated here were given neither food nor water until they were dead.[12]

In the basement were the "dark cells"; these cells had only a very tiny window, and a solid door. Prisoners placed in these cells would gradually suffocate as they used up all of the oxygen in the cell; sometimes the SS would light a candle in the cell to use up the oxygen more quickly. Many were subjected to hanging with their hands behind their backs, thus dislocating their shoulder joints for hours, even days.[13]
On September 3, 1941, deputy camp commandant SS-Hauptsturmführer Fritzsch experimented on 600 Russian POWs and 250 Polish inmates by gathering them in the basement of Block 11 and gassing them with Zyklon B, a highly lethal cyanide-based pesticide.[14] This paved the way for the use of Zyklon B as an instrument for extermination at Auschwitz, and a gas chamber and crematorium were constructed by converting a bunker. This gas chamber operated from 1941 to 1942, during which time some 60,000 people were killed therein; it was then converted into an air-raid shelter for the use of the SS. This gas chamber still exists, together with the associated crematorium, which was reconstructed after the war using the original components, which remained on-site.
Auschwitz II-Birkenau

Construction on Auschwitz II-Birkenau, the extermination camp, began in October 1941 to ease congestion at the main camp. It was larger than Auschwitz I, and more people passed through its gates than through Auschwitz I. It was designed to hold several categories of prisoners, and to function as an extermination camp in the context of Heinrich Himmler's preparations for the Final Solution of the Jewish Question, the extermination of the Jews.[15] The first gas chamber at Birkenau was "The Little Red House," a brick cottage converted into a gassing facility by tearing out the inside and bricking up the walls. It was operational by March 1942. A second brick cottage, "The Little White House," was similarly converted some weeks later.[16]
The Nazis had committed themselves to the final solution no later than January 1942, the date of the Wannsee Conference. In his Nuremberg testimony on April 15, 1946, Rudolf Höss, the commandant of Auschwitz, testified that Heinrich Himmler personally ordered him to prepare Auschwitz for that purpose:
In the summer of 1941 I was summoned to Berlin to Reichsführer-SS Himmler to receive personal orders. He told me something to the effect—I do not remember the exact words—that the Fuehrer had given the order for a final solution of the Jewish question. We, the SS, must carry out that order. If it is not carried out now then the Jews will later on destroy the German people. He had chosen Auschwitz on account of its easy access by rail and also because the extensive site offered space for measures ensuring isolation.[17]

British historian Laurence Rees writes, that Höss may have misremembered the year Himmler said this. Himmler did indeed visit Höss in the summer of 1941, but there is no evidence that the final solution had been planned at this stage. Rees writes that the meeting predates the killings of Jewish men by the Einsatzgruppen in the East and the expansion of the killings in July 1941. It also predates the Wannsee Conference. Rees speculates that the conversation with Himmler was most likely in the summer of 1942.[18] The first gassings, using an industrial gas derived from prussic acid and known by the brand name Zyklon-B, were carried out at Auschwitz in September 1941.[19]
In early 1943, the Nazis decided to increase greatly the gassing capacity of Birkenau. Crematorium II, originally designed as a mortuary, with morgues in the basement and ground-level furnaces, was converted into a killing factory by placing a gas-tight door on the morgues and adding vents for Zyklon B and ventilation equipment to remove the gas.[20] It went into operation in March. Crematorium III was built using the same design. Crematoria IV and V, designed from the start as gassing centers, were also constructed that spring. By June 1943 all four crematoria were operational. Most of the victims were killed during the period afterwards.[21]
The camp was staffed partly by prisoners, some of whom were selected to be kapos (orderlies, most of whom were convicts) and sonderkommandos (workers at the crematoria). The kapos were responsible for keeping order in the barrack huts; the sonderkommandos prepared new arrivals for gassing (ordering them to remove their clothing and surrender their personal possessions) and transferred corpses from the gas chambers to the furnaces, having first pulled out any gold that the victims might have had in their teeth. Members of these groups were killed periodically. The kapos and sonderkommandos were supervised by members of the SS; altogether 6,000 SS members worked at Auschwitz.
Command of the women's camp, which was separated from the men's area by the incoming railway line, was held in turn by Johanna Langefeld, Maria Mandel, and Elisabeth Volkenrath.
Auschwitz III
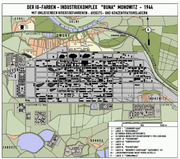
The largest of the Auschwitz work camps was Auschwitz III-Monowitz, named after the Polish village of Monowice, and regarded from the fall of 1943 onwards as an industrial camp. Starting operations in May 1942, it was associated with the synthetic rubber and liquid fuel plant Buna-Werke owned by IG Farben. 11,000 slave laborers worked at Monowitz. Seven thousand inmates worked at various chemical plants. 8,000 worked in mines. Approximately 40,000 prisoners worked in slave labor camps at Auschwitz or nearby, under appalling conditions.[22] In regular intervals, doctors from Auschwitz II would visit the work camps and select the weak and sick for the gas chambers of Birkenau.
Subcamps

There were 45 smaller satellite camps, some of them tens of kilometers from the main camps, with prisoner populations ranging from several dozen to several thousand.[23] The largest were built at Trzebinia, Blechhammer and Althammer. Women's subcamps were constructed at Budy, Pławy, Zabrze, Gleiwitz I, II, III, Rajsko, and Lichtenwerden (now Světlá). The satellite camps were named Aussenlager (external camp), Nebenlager (extension or subcamp), and Arbeitslager (labor camp).[23] Danuta Czech of the Auschwitz-Birkenau State Museum writes that most of the satellite camps were pressed into service on behalf of German industry. Inmates of 28 of them worked for the German armaments industry. Nine camps were set up near foundries and other metal works, six near coal mines, six supplied prisoners to work in chemical plants, and three to light industry. One was built next to a plant making construction materials and another near a food processing plant. Apart from the weapons and construction industries, prisoners were also made to work in forestry and farming.[24]
Selection process and genocide

By July 1942, the SS were conducting the infamous "selections," in which incoming Jews were divided into those deemed able to work, who were sent to the right and admitted into the camp, and those who were sent to the left and immediately gassed.[26] Prisoners were transported from all over German-occupied Europe by rail, arriving in daily convoys. The group selected to die, about three-quarters of the total, included almost all children, women with children, all the elderly, and all those who appeared on brief and superficial inspection by an SS doctor not to be completely fit. Auschwitz II-Birkenau claimed more victims than any other German extermination camp, despite coming into use after all the others.
.jpg)
SS officers told the victims they were to take a shower and undergo delousing. The victims would undress in an outer chamber and walk into the gas chamber, which was disguised as a shower facility, complete with dummy shower heads. After the doors were shut, SS men would dump in the cyanide pellets via holes in the roof or windows on the side. In Auschwitz II-Birkenau, more than 20,000 people could be gassed and cremated each day. The Nazis used a cyanide gas produced from Zyklon B pellets, manufactured by two companies who had acquired licensing rights to the patent held by IG Farben.

Sonderkommandos removed gold teeth from the corpses of gas chamber victims; the gold was melted down and collected by the SS. The belongings of the arrivals were seized by the SS and sorted in an area of the camp called "Canada," so-called because Canada was seen as a land of plenty. Many of the SS at the camp enriched themselves by pilfering the confiscated property.[27]
The gas chambers worked to their fullest capacity from April-July 1944, during the massacre of Hungary's Jews. Hungary was an ally of Germany during the war, but it had resisted turning over its Jews to the Germans until Germany invaded in March 1944. From April until July 9, 1944, 475,000 Hungarian Jews, half of the pre-war population, were deported to Auschwitz, at a rate of 12,000 a day for a considerable part of that period.[28] The incoming volume was so great that the SS resorted to burning corpses in open-air pits as well as in the crematoria.[29]
Life in the camps
The prisoners' day began at 4:30 a.m. with "reveille" or roll call, with 30 minutes allowed for morning ablutions. After roll call, the Kommando, or work details, would walk to their place of work, five abreast, wearing striped camp fatigues, no underwear, and wooden shoes without socks, most of the time ill-fitting, which caused great pain. An orchestra often played as the workers marched through the gates. Kapos—prisoners who had been promoted to foremen—were responsible for the prisoners' behavior while they worked, as was an SS escort. The working day lasted 12 hours during the summer, and a little less in the winter. No rest periods were allowed. One prisoner would be assigned to the latrines to measure the time the workers took to empty their bladders and bowels.[30]
After work, there was a mandatory evening roll call. If a prisoner was missing, the others had to remain standing in place until he was either found or the reason for his absence discovered, even if it took hours, regardless of the weather conditions. After roll call, there were individual and collective punishments, depending on what had happened during the day, and after these, the prisoners were allowed to retire to their blocks for the night to receive their bread rations and water. Curfew was two or three hours later, the prisoners sleeping in long rows of wooden bunks, lying in and on their clothes and shoes to prevent them from being stolen.[31]
Medical experiments

German doctors performed a wide variety of experiments on prisoners at Auschwitz. SS doctors tested the efficacy of X-rays as a sterilization device by administering large doses to female prisoners. Prof. Dr. Carl Clauberg injected chemicals into women's uteruses in an effort to glue them shut. Bayer, then a subsidiary of IG Farben, bought prisoners to use as guinea pigs for testing new drugs.[32]
The most infamous doctor at Auschwitz was Josef Mengele, known as the "Angel of Death". Particularly interested in research on identical twins, Mengele performed cruel experiments on them, such as inducing diseases in one twin and killing the other when the first died to perform comparative autopsies. He also took a special interest in dwarfs and deliberately infected twins, dwarfs and other prisoners with gangrene to "study" the effects.[33]
Mengele, at the behest of fellow Nazi physcian Kurt Heissmeyer, was responsible for picking the twenty Jewish children to be used in Heissmeyers' pseudoscientific medical experiments at the Neuengamme concentration camp. These children, at the conclusion of the experiments, were infamously hung from wall hooks in the basement of the Bullenhuser Damm school in Hamburg.
Jewish skeleton collection
The Jewish skeleton collection was obtained from among a pool of 115 inmates at Auschwitz, chosen for their racial characteristics. Rudolf Brandt and Wolfram Sievers, general manager of the Ahnenerbe, were responsible for collecting the skeletons for the collection of the Anatomy Institute at the Reich University of Strasbourg in the Alsace region of Occupied France. Due to a typhus epidemic, the candidates chosen for the skeleton collection were quarantined in order to prevent them from becoming ill and ruining their value as anatomical specimens; from a letter written by Sievers in June 1943: "Altogether 115 persons were worked on, 79 were Jews, 30 were Jewesses, 2 were Poles, and 4 were Asiatics. At the present time these prisoners are segregated by sex and are under quarantine in the two hospital buildings of Auschwitz."
The collection was sanctioned by Heinrich Himmler and under the direction of August Hirt.
Ultimately 86 of the inmates were shipped to Natzweiler-Struthof. The deaths of these 86 inmates was, in the words of Hirt, "induced" at a jury rigged gassing facility, at Natzweiler-Struthof on July 30, 1943 and their corpses; 57 men and 29 women were sent to Strasbourg. Josef Kramer who would become the last commandant of Bergen Belsen personally carried out the gassing. In 1944 with the approach of the allies, there was concern over the possibility of the corpses being discovered, at this point they had still not been defleshed. The first part of the process for this "collection" was to make anatomical casts of the bodies prior to reducing them to skeletons. In September, 1944 Sievers telegrammed Brandt: "The collection can be defleshed and rendered unrecognizable. This, however, would mean that the whole work had been done for nothing-at least in part-and that this singular collection would be lost to science, since it would be impossible to make plaster casts afterwards."
Brandt and Sievers would be indicted, tried and convicted in the Doctor's Trial in Nuremberg. Hirt committed suicide in Schonenbach, Austria, on June 2, 1945 with a gunshot to the head.[34][35] The names and biographical information of the murder victims were published in the book Die Namen der Nummern (The Names of the Numbers) by German historian Dr. Hans-Joachim Lang.[36]
Escapes, resistance, and the Allies' knowledge of the camps

Information regarding Auschwitz was available to the Allies during the years 1940–1943 by accurate and frequent reports of Polish Army Captain Witold Pilecki. Pilecki was the only known person to volunteer to be imprisoned at Auschwitz concentration camp, spending 945 days at Auschwitz not only actively gathering evidence of genocide and supplying it to the British in London by Polish resistance movement organization Home Army but also organizing resistance structures at the camp known as ZOW, Związek Organizacji Wojskowej.[37] His first report was smuggled outside in November 1940. He eventually escaped on April 27, 1943, but his personal report of mass killings was dismissed as exaggeration by the Allies, as were his previous ones.[38]

The attitude of the Allies changed with receipt of the very detailed Vrba-Wetzler report, compiled by two Jewish prisoners, Rudolf Vrba and Alfred Wetzler, who escaped on April 7, 1944, and which finally convinced Allied leaders of the truth about Auschwitz. Details from the Vrba-Wetzler report were broadcast on June 15, 1944 by the BBC, and on June 20 by The New York Times, causing the Allies to put pressure on the Hungarian government to stop the mass deportation of Jews to the camp.[39]
Starting with a plea from the Slovakian rabbi Weissmandl in May 1944, there was a growing campaign to persuade the Allies to bomb Auschwitz or the railway lines leading to it. At one point Winston Churchill ordered that such a plan be prepared, but he was told that bombing the camp would most likely kill prisoners without disrupting the killing operation, and that bombing the railway lines was not technically feasible. The debate over what could have been done, or what should have been attempted even if success was unlikely, has continued ever since.
Birkenau revolt

By 1943, resistance organizations had developed in the camp. These organizations helped a few prisoners escape; these escapees took with them news of exterminations, such as the killing of hundreds of thousands of Jews transported from Hungary between May and July 1944. On October 7, 1944, the Jewish Sonderkommandos (those inmates kept separate from the main camp and put to work in the gas chambers and crematoria) of Birkenau Kommando III staged an uprising. They attacked the SS with makeshift weapons: stones, axes, hammers, other work tools and homemade grenades. They caught the SS guards by surprise, overpowered them and blew up the Crematorium IV, using explosives smuggled in from a weapons factory by female inmates. At this stage they were joined by the Birkenau Kommando I of the Crematorium II, which also overpowered their guards and broke out of the compound. Hundreds of prisoners escaped, but were all soon captured and, along with an additional group who participated in the revolt, executed.[40]
There were also plans for a general uprising in Auschwitz, coordinated with an Allied air raid and a Polish resistance (Armia Krajowa, Home Army) attack from the outside.[38] That plan was authored by Polish resistance fighter, Witold Pilecki, who organized in Auschwitz an underground Union of Military Organization - (Związek Organizacji Wojskowej, ZOW). Pilecki and ZOW hoped that the Allies would drop arms or troops into the camp (most likely the Polish 1st Independent Parachute Brigade, based in Britain), and that the Home Army would organize an assault on the camp from outside. By 1943, however, he realized that the Allies had no such plans. Meanwhile, the Gestapo redoubled its efforts to ferret out ZOW members, succeeding in killing many of them. Pilecki decided to break out of the camp, with the hope of personally convincing Home Army leaders that a rescue attempt was a valid option. He escaped on the night of April 26–April 27, 1943, but his plan was not accepted by the Home Army as the Allies considered his reports about the Holocaust exaggerated.[38]
Individual escape attempts
At least 802 prisoners attempted to escape from the Auschwitz camps during the years of their operation, of which 144 were successful. The fates of 331 of the escapees are still unknown.[41] A common punishment for escape attempts was death by starvation; the families of successful escapees were sometimes arrested and interned in Auschwitz and prominently displayed to deter others. If someone did manage to escape, the SS would pick 10 random people from the prisoner's block and starve them to death.[42]
Since the concentration camps were designed to degrade prisoners beneath human dignity, maintaining the will to survive was seen in itself as an act of rebellion. Primo Levi was taught this lesson by his fellow prisoner and friend Steinlauf:
[that] "precisely because the camp was a great machine to reduce us to beasts, we must not become beasts; that even in this place one can survive, and therefore one must want to survive, to tell the story, to bear witness; and that, if we want to survive, then it's important that we strive to preserve at least the skeleton, the scaffolding, the external shape of civilization."[43]
The most spectacular escape from Auschwitz took place on 20 June 1942, when Ukrainian Eugeniusz Bendera and three Poles, Kazimierz Piechowski, Stanisław Gustaw Jaster and Józef Lempart made a daring escape.[44] The escapees were dressed as members of the SS-Totenkopfverbände, fully armed and in an SS staff car. They drove out the main gate in a stolen automobile, a Steyr 220 belonging to Rudolf Hoss. Jaster carried with him a report about conditions in the camp, written by Witold Pilecki. The Germans never recaptured any of them.[45]
In 1943, the "Kampfgruppe Auschwitz" was organised with the aim to send out as much information about what was happening in Auschwitz as possible. They buried notes in the ground in the hope a liberator would find them and smuggled out photos of the crematoria and gas chambers.[46]
June 24, 1944, Mala Zimetbaum escaped with her Polish boyfriend, Edek Galinski. They also wanted to smuggle out deportation lists Zimetbaum had been able to copy due to her translator job in the office of the "Lagerleitung". They both were arrested on July 6 near the Slovakian frontier and sentenced to be executed on September 15, 1944 in Birkenau; Galinski managed to kill himself before being executed, while Zimetbaum, having failed to commit suicide, died finally after being tortured by the SS.[47]
Evacuation, death marches, and liberation

The last selection took place on October 30, 1944. The next month, Heinrich Himmler ordered the crematoria destroyed before the Red Army reached the camp. The gas chambers of Birkenau were blown up by the SS in January 1945 in an attempt to hide the German crimes from the advancing Soviet troops. The SS command sent orders on January 17, 1945 calling for the execution of all prisoners remaining in the camp, but in the chaos of the Nazi retreat the order was never carried out. On January 17, 1945, Nazi personnel started to evacuate the facility. Nearly 60,000 prisoners were forced on a death march toward a camp in Wodzisław Śląski (German: Loslau). Those too weak or sick to walk were left behind. These remaining 7,500 prisoners were liberated by the 322nd Rifle Division of the Red Army on January 27, 1945. Approximately 20,000 Auschwitz prisoners made it to Bergen-Belsen concentration camp in Germany, where they were liberated by the British in April 1945.[48] Among the artifacts of automated murder found by the Russians were 348,820 men's suits and 836,255 women's garments.[22]
Death toll

The exact number of victims at Auschwitz is impossible to fix with certainty. Since the Nazis destroyed a number of records, immediate efforts to count the dead depended on the testimony of witnesses and the defendants on trial at Nuremberg. While under interrogation Rudolf Höss, commandant of Auschwitz concentration camp from 1940 to 1943, said that Adolf Eichmann told him that two and a half million Jews had been killed in gas chambers and about half a million had died "naturally". Later he wrote "I regard two and a half million far too high. Even Auschwitz had limits to its destructive possibilities".[49]
Communist Polish and Soviet authorities maintained a figure "between 2.5 and 4 million",[50] and the Auschwitz State Museum itself displayed a figure of 4 million killed, but "[f]ew (if any) historians ever believed the Museum's four million figure".[51] Raul Hilberg's 1961 work The Destruction of the European Jews estimated the number killed at 1,000,000, and Gerald Reitlinger's 1968 book The Final Solution described the Soviet figures as "ridiculous", and estimated the number killed at "800,000 to 900,000".[52] A larger study started later by Franciszek Piper used timetables of train arrivals combined with deportation records to calculate 960,000 Jewish deaths and 140,000-150,000 ethnic Polish victims, along with 23,000 Roma and Sinti (Gypsies),[53] a figure that has met with significant agreement from other scholars.[54]
After the collapse of the Communist government in 1989, the plaque at Auschwitz State Museum was removed and the official death toll given as 1.1 million. Holocaust deniers have attempted to use this change as propaganda, in the words of the Nizkor Project:
Deniers often use the 'Four Million Variant' as a stepping stone to leap from an apparent contradiction to the idea that the Holocaust was a hoax, again perpetrated by a conspiracy. They hope to discredit historians by making them seem inconsistent. If they can't keep their numbers straight, their reasoning goes, how can we say that their evidence for the Holocaust is credible? One must wonder which historians they speak of, as most have been remarkably consistent in their estimates of a million or so dead... Few (if any) historians ever believed the Museum's four million figure, having arrived at their own estimates independently. The museum's inflated figures were never part of the estimated five to six million Jews killed in the Holocaust, so there is no need to revise this figure.[51]
Timeline of events in Auschwitz
The timeline of events of the Auschwitz concentration camp began in January 1940 when the location was first visited by Arpad Wigand an aid to the Higher SS and Police Leader for Silesia Erich von dem Bach Zelewski. The original intent of the camp was to intern Polish political prisoners. The original uses of the camp were added to and the capacity expanded over the course of the next four years, which reflected the political and economic decisions of the Third Reich, including the implementation of the Final Solution.
| Timeline of Events in Auschwitz | ||
|---|---|---|
| February 21, 1940 | In January Arpad Wigand aide to Höhere SS- und Polizeiführer for Silesia Erich von dem Bach Zelewski suggests the Polish military barracks at Oświęcim as a site for a concentration camp for Polish prisoners. Inspector of concentration camps Richard Glucks sends Sachenhausen commandant Walter Eisfeld to inspect the site. On Feb. 21 Glucks informs Reichsfuhrer SS Heinrich Himmler that the site will be developed into a concentration camp.[55] | |
May 20, 1940 |
The first prisoners, 30 German career criminals from Sachsenhausen, arrive. Most will be made kapos, prisoner no. 1 is a German of Polish descent Bruno Brodniewicz. Among this group is Kurt Pachala from Breslau (prisoner no. 24) who was tortured and then sent to a "standing cell" in the basement of Block 11 where he died of thirst and hunger on Jan. 14, 1943 as punishment for the June 20, 1942 escape of four prisoners.[56] | |
| June 14, 1940 | First mass transport, consisting of 728 Polish political prisoners from Tarnow. They are held in the building which housed the Polish Tobacco Monopoly, until the camp is ready. Among the prisoners is Edward Galinski who would later make an escape with his girlfriend.[58] | |
| March 1, 1941 |
Reichsführer SS and Chief of German Police Heinrich Himmler inspects the camp. Because nearby factories use prisoners for forced labor, Himmler is concerned about the camp's capacity. On this visit, he orders both the expansion of Auschwitz I camp facilities to hold 30,000 prisoners and the building of a camp near Birkenau for an expected influx of 100,000 Soviet prisoners of war. Himmler also orders that the camp supply 10,000 prisoners for forced labor to construct an IG Farben factory complex at Dwory, about a mile away. Himmler made additional visits to Auschwitz in 1942, when he witnessed the killing of prisoners in the gas chambers. | |
September 3, 1941 |
The first gassings of prisoners occur in Auschwitz I. The SS tests Zyklon B gas by killing 600 Soviet prisoners of war and 250 other ill or weak prisoners. Testing takes place in a makeshift gas chamber in the cellar of Block 11 in Auschwitz I. The success of these experiments leads to the adoption of Zyklon B as the killing agent for Auschwitz II-Birkenau. | |
January 25, 1942 |
Himmler informs Richard Gluecks, the Inspector of Concentration Camps, that 100,000 Jewish men and 50,000 Jewish women are to be deported from Germany to Auschwitz as forced laborers. | |
June 20, 1942 |
Polish political prisoner, Kazimierz Piechowski (prisoner no. 18), and three other prisoners, Stanisław Gustaw Jaster, Józef Lempart, and Eugeniusz Bendera, made a brazen escape. They managed to steal SS uniforms and weapons, they stole Rudolf Hoess' car from the motor pool and drove out the main gate. The escape was facilitated by Piechowski's fluent command of German, as they drove toward the gate he told the guards to hurry up and open it. None of the four were recaptured.[59] | |
February 15, 1942 |
The first transport of Jews from Bytom (Beuthen) in German-annexed Upper Silesia arrives in Auschwitz I. The SS camp authorities kill all those on the transport immediately upon arrival with Zyklon B gas. German SS and police authorities deport around 175,000 Jews to Auschwitz in 1942. | |
| January 1, 1943–March 31, 1943 | German SS and police authorities deport approximately 105,000 Jews to Auschwitz | |
January 29, 1943 |
The Reich Central Office for Security orders all designated Roma (Gypsies) residing in Germany, Austria, and the Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia to be deported to Auschwitz. | |
| February 26, 1943 | The first transport of Roma from Germany arrives. The SS authorities house them in Section B-IIe of Auschwitz-Birkenau, which becomes known as the "Gypsy family camp." By the end of 1943 more than 18,000 Roma were incarcerated there, and 23,000 deported to other parts of the camp complex. | |
March 13, 1943 |
Out of a transport of 2,000 Jews from the Kraków Ghetto, 1,492 are gassed in the basement gas chamber of Crematorium II at Birkenau in the evening. This operation tests the gas chamber's ventilation and air extraction equipment installed by J.A. Topf engineer Heinrich Messing, who declared it operational earlier that day.[60] | |
| March 22, 1943 | Crematorium IV is ready for use.[61] | |
March 31, 1943 |
Crematorium II is handed over to the Auschwitz authorities.[60] Holocaust scholar Robert Jan van Pelt comments that more people lost their lives in this room than in any other room on Earth: 500,000 people.[62] | |
| April 4, 1943 | Crematorium V is ready for use.[61] | |
April 22, 1943 |
Transport 20 from the transit camp in Mechelen, Belgium arrives in Auschwitz. A Jewish doctor Youra Livschitz and his two non-Jewish high school friends Robert Maistriau and Jean Franklemon managed to stop the train on the tracks with only a lantern and a handgun when it rounded a curve in Boortmeerbeek, Belgium and open the doors on some of the rail cars. Some prisoners managed to escape then, over 200 more jumped from the train en route.[63] | |
| April 26–27, 1943 | Witold Pilecki escapes during the night. He would later take part in the Warsaw Uprising, get captured and spend the remainder of the war in P.O.W. camps. | |
May 30, 1943 |
Josef Mengele arrives at Auschwitz. He often took part in "selections" of incoming prisoners on the ramp at Birkenau. During his time at Aushwitz he engaged in pseudoscientific experiments on camp inmates. He had a special fascination with twins. Mengele was known as "the Angel of Death". He escaped to South America after the war and was never brought to justice.[64] | |
June 24, 1943.jpg) |
Crematorium III is ready for use.[65] | |
July 19, 1943 |
Largest mass hanging at Aushwitz, public gallows constructed of train rails and railroad ties, specifically constructed to simultaneously hang 12 Polish prisoners, part of the Survey Kommando, for helping three prisoners escape. Two of the hanged are Boguslaw Ohrt: [no. 367] and Janusz Pogonowskino [no.253] [66] |
|
| February 21, 1944 | Primo Levi arrives in the camp from Italy. | |
| April 7, 1944 | Two Jewish prisoners, Rudolf Vrba and Alfréd Wetzler, escape and pass a 32-page report of what is happening in the camp to Jewish officials in Slovakia. Their information becomes known as the Vrba-Wetzler report. | |
May 2, 1944 |
The first two transports of Hungarian Jews arrive in Auschwitz. Throughout May and June 1944, Hungarian Jews are deported to the camp at a rate of 12,000 a day. | |
May 16, 1944 |
Elie Wiesel arrives with his family on or around this date. His mother and youngest sister are immediately sent to be gassed. | |
May 22, 1944 |
Romani-Sinti, deported from the Netherlands arrive in Auschwitz-Birkenau. Settela Steinbach an eleven year old Sinti girl is caught on film peering out from the transport on May 19, by Jewish prisoner Rudolf Breslauer, who was ordered to film the deportation by the commandant of the Westerbork transit camp. Settela would die in the gas chamber. | |
| June 6, 1944 | The Allies land in Normandy, France to begin the liberation of Western Europe. | |
June 24, 1944 |
Polish born Jewish girl Mala Zimetbaum (prison no.19880) and her Polish boyfriend Edward "Edek" Galinski (prison no. 518) escape from Birkenau. Galinski, one of the first deportees to Auschwitz, was wearing an SS uniform provided to him by SS-Rottenfuehrer Edward Lubusch, an ethnic German raised in Poland. They were caught on July 6, 1944 and returned to Auschwitz. They were imprisoned in separate cells in Block 11; both were sentenced to death. On September 15, 1944, Galinski was hung. Mala slit her wrists with a razor blade interrupting her execution. She was, according to various accounts taken to the crematorium to be burned alive. It's not known whether that occurred or she was shot in the crematorium.[67][68] | |
July 7, 1944 |
In response to the publication of the Vrba-Wetzler Report, governments around the world put pressure on Regent Miklós Horthy of Hungary to halt the deportation of Hungarian Jews to Auschwitz, which he does on July, 7 1944 | |
August 2–3, 1944 |
The Gypsy family camp is liquidated during the night; 2,897 men women and children perish in the gas chamber, 1,400 surviving men and women are transferred to Buchenwald and Ravensbruck for slave labor. An estimated 20,000 Roma were killed there in Aushwitz. Among the murdered are Romani mischlinge, used by Nazi race scientist Eva Justin in her pseudoscientific race research. | |
August 12–13, 1944 |
Almost 6,000 residents of Warsaw are transported to Auschwitz in response to the Warsaw Uprising (approximately twice as many females as males, including over a thousand children). | |
September 3, 1944 |
Anne Frank is transported to Auschwitz along with her mother Edith and sister Margot; on October 28, 1944 Anne and Margot were chosen in a selection to be transferred to Bergen-Belsen. Edith was left behind where it was reported she died of starvation. Anne and Margot would both die in March 1945 in the Typhus epidemic at Bergen-Belsen only weeks before the camp's liberation by the British on April 15, 1945.[69] | |
| September 4, 1944 | A transport of 3,087 predominantly Polish men, women, and children from Warsaw arrive in Auschwitz in retribution for Warsaw uprising | |
| September 13 and 17, 1944 | Another 4,000 predominantly Polish men and boys from Warsaw arrive in Auschwitz as retribution for the uprising. | |
October 7, 1944 |
Members of the Jewish prisoner "special detachment" (Sonderkommando) that was forced to remove bodies from the gas chambers and operate the crematoria stage an uprising. They successfully blow up Crematorium IV and kill several guards. Women prisoners had smuggled gunpowder out of nearby factories to members of the Sonderkommando. The SS quickly suppresses the revolt and kills all the Sonderkommando members. | |
October 30, 1944 |
The last selections take place on the Jewish ramp at Birkenau; 1,689 people from a transport from Terezin are sent to the gas chambers. After this, only individuals are gassed after selection within the camp. The last 13 people to be killed this way were women, gassed or shot in crematorium II on November 25.[70] | |
| November 25, 1944 |
As Soviet forces approach, SS chief Heinrich Himmler orders the destruction of the Auschwitz-Birkenau gas chambers and crematoria. During this attempt to destroy the evidence of mass killings, prisoners are forced to dismantle and dynamite the structures. | |
November 27, 1944 |
Twenty Jewish children, 10 boys and 10 girls ages 5–12, are selected from Block 10, by Josef Mengele at the behest of Kurt Heissmeyer. The children are sent to Neuengamme concentration camp. There they are infected with tuberculosis and subjected to medical experimentation. They are ultimately murdered by being hanged in the basement of the Bullenhuser Damm school in Hamburg.[71] | |
January 12, 1945 |
The Red Army launches the Vistula-Oder Offensive ; Soviet troops liberate Lodz on January 17, only 877 Jews remain in the ghetto out of a high of 163,177 people in 1941; Warsaw and Kraków are both liberated on January, 19. The advance heads toward Oświęcim. | |
January 18–27, 1945 |
As Soviet units approach the camp, the SS evacuates prisoners to the west. Tens of thousands, mostly Jews, are forced to march to the cities of Loslau and Gleiwitz) in Upper Silesia. During the march, SS guards shoot anyone who cannot continue. In Loslau and Gleiwitz, the prisoners are placed on unheated freight trains and deported to concentration camps in Germany, particularly to Flossenburg, Sachsenhausen, Gross-Rosen, Buchenwald, and Dachau, and to Mauthausen in Austria. Nearly 60,000 prisoners are forced on death marches from the Auschwitz camp system. As many as 15,000 die. Thousands more are killed in the days before the evacuation. | |
January 27, 1945 |
Soviet troops enter the Auschwitz camp complex and liberate 7,000 prisoners, including children. | |
| March 11, 1946 | British troops capture the camp's first commandant, Rudolf Höss, who is living as a farmer called Franz Lang. | |
April 16, 1947 |
Poland sentences Rudolf Höss to death on April 2, 1947 and he is hanged on April 16. | |
After the war
After the war parts of Auschwitz 1 and/or its guards' quarters served first as a hospital for sick liberated prisoners.[72] After that until 1947 parts were used as an NKVD and MBP prison camp. The Buna-Werke were taken over by the Polish government and became the foundation for the region's chemical industry.
At Auschwitz 1 the Gestapo building was demolished and on its site was built a gallows on which Standartenführer SS Rudolf Höss was hanged on 17 April 1947 for many crimes.[73]
Today, at Birkenau the entrance building and some of the southern brick-built barracks survive; but of the almost 300 wooden barracks, only 19 remain: 18 near the entrance building and one, on its own, farther away. All that survives of the others are chimneys, remnants of a largely ineffective means of heating. Many of these wooden buildings were constructed from prefabricated sections made by a company that intended them to be used as stables; inside, numerous metal rings for the tethering of horses can still be seen.
Creation of the museum

The Polish government decided to restore Auschwitz I and turn it into a museum honouring the victims of Nazism; Auschwitz II, where buildings (many of which were prefabricated wood structures) were prone to decay, was preserved but not restored. Today, the Auschwitz I museum site combines elements from several periods into a single complex: for example the gas chamber at Auschwitz I (which had been converted into an air-raid shelter for the SS) was restored and the fence was moved (because of building work being done after the war but before the museum was established). However, in most cases the departure from the historical truth is minor, and is clearly labelled. The museum contains many men's, women's and children's shoes taken from their victims; also suitcases, which the deportees were encouraged to bring with them, and many household utensils. One display case, some 30 metres (98 ft) long, is wholly filled with human hair which the Nazis gathered from people before they were sent to labor or before and after they were killed.
Auschwitz II and the remains of the gas chambers there are open to the public. The camp is on the list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites. The ashes of the victims were scattered between the huts, and the entire area is regarded as a grave site. Most of the buildings of Auschwitz I are still standing. The public entrance area is outside the perimeter fence in what was the camp admission building, where new prisoners were registered and given their uniforms. At the far end of Birkenau are memorial plaques in many languages, including Romani.
The museum has allowed scenes for three films to be filmed on the site: Pasażerka (1963) by Polish director Andrzej Munk, Landscape After the Battle (1970) by Polish director Andrzej Wajda, and a television miniseries War and Remembrance (1978). Permission was denied to Steven Spielberg to film scenes for Schindler's List (1993). A "mirror" camp was constructed outside the infamous archway for the scene where the train arrives carrying the women who were saved by Oskar Schindler.
"Arbeit macht frei" sign theft
The 5-metre (16 ft), 41-kilogram (90 lb) wrought-iron "Arbeit macht frei" sign over the entrance to Auschwitz I was stolen in the early morning of December 18, 2009. The thieves unscrewed the sign at one end and broke it off its mountings at the other end, then carried the sign 300 metres to a hole in the concrete wall, where they cut four metal bars blocking the opening. After the theft, authorities replaced the stolen sign with a replica, which was originally made to replace the original sign while it was being restored some years earlier.[74] Such was the concern about its theft that Poland declared a state of emergency.[75] Police found the sign, cut into three parts, in northern Poland two days later in the home of one of five men who were arrested. An unnamed overseas buyer is believed to have been involved.[76] Polish police said that the five were common thieves, not neo-Nazis.[77][78] The original sign has been welded back together and put back up after an improved security system is put in place.[79] [80]
The sign was made by Polish workers on Nazi orders after the Auschwitz barracks were converted into a labor camp to house captured Polish resistance fighters in 1940.[81]
The Aftonbladet newspaper reported that the sign had been stolen by Polish thieves paid by and working on behalf of a Swedish right-wing extremist group hoping to use proceeds from the proposed sale of the sign to a collector of Nazi memorabilia, to finance a series of terror attacks aimed at influencing voters in upcoming Swedish parliamentary elections.[82][83] The theft was organised by the Swedish former Nazi, Anders Högström.[84]
On March 18, 2010, a Polish court sentenced three men to prison for stealing the sign. They pleaded guilty. The sentences were from 18 months to 30 months. They were fined £2,300 each.[85] Two of them were granted compassionate leave, but in April the three did not report to the prison to serve their sentences, and police were trying to find them.[86][87][88]
May-June 2010 flood
In the 2010 Central European floods staff had to close the museum and move documents and relics to upper floors.[89]
Gallery
 Auschwitz I in winter |
 Interior of the gas chamber of Auschwitz I |
 Interior of the crematorium of Auschwitz I. This facility was much smaller than those of Auschwitz II. |
Surreptitious photo taken by a member of the Sonderkommando, women undressed and sent to gas chamber |
 Roll call in front of the camp kitchen, 1944 |
 Auschwitz II-Birkenau in 2009 |
 Auschwitz II-Birkenau ruins in 2009 |
 Rudolf Höss (1900-1947), the first commandant of Auschwitz |
|
Josef Kramer (1906-1945), Höss's first deputy |
 Block 11, execution wall seen in courtyard, through archway |
 Execution wall in Auschwitz I, between blocks 10 and 11 |
 Eyeglasses of victims |
 Exhibit of shoes from the victims of Auschwitz |
 Elie Wiesel was 15 when he arrived in the camp around May 16, 1944. |
 Gas chamber in Auschwitz I |
 Jews from Carpathian Ruthenia arriving at Auschwitz-Birkenau |
 Bunk beds in Auschwitz II. There were as many as four inmates per bunk. There could be as many as a thousand inmates per barrack. |
 Elisabeth Klein; one of the 86 victims in the "Jewish skeleton collection" |
 Burning corpses; surreptitious photograph taken by a member of the Sonderkommando |
Entrance to Birkenau, 2006. Guard tower, two information boards seen on the left. |
|
Israeli Defense Forces ceremony near the entrance of Auschwitz |
See also
- Central Labour Camp Jaworzno Arbeitslager Neu-Dachs (Jaworzno)
- Auschwitz Album - a collection of pictures taken at Auschwitz during its operation.
- Auschwitz Trial
- Frankfurt Auschwitz Trials
- Höcker Album
- International Auschwitz Committee
- List of inmates and victims of Auschwitz
- List of Nazi concentration camps
- Oświęcim synagogue
- Przyszowice massacre
- Survivor syndrome
Notes
- ↑ Krakowski 1994, p. 50.
- ↑ Gutman 1992, p. 6.
- ↑ Trials of the Major War Criminals Before the International Military Tribunal, Nuremberg 14 November 1945 - 1 October 1946, Volume 1, Page 251
- ↑ Piper 1994, pp. 68-70.
- ↑ Swiebocka, Teresa. Report from Workshop 1 on Remembrance and Representation: Presentation by Teresa Swiebocka, Stockholm International Forum on the Holocaust, 2000. Retrieved December 22, 2009.
- ↑ Piper 1994, p. 62.
- ↑ "Auschwitz Hero Denis Avey in Line for Israeli Honour" BBC, Dec. 30, 2009
- ↑ Primo Levi quoted in Gutman 1994, p. 5.
- ↑ Rees 2009, BBC.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Gutman 1994, pp. 10, 16.
- ↑ Wittmann 2003.
- ↑ "Maximilian Kolbe". Jewishvirtuallibrary.org. http://www.jewishvirtuallibrary.org/jsource/biography/Kolbe.html. Retrieved 2010-08-23.
- ↑ Rees 2005, p. 26.
- ↑ (English) Muzeum Auschwitz-Birkenau w Oświęcimiu
- ↑ Gutman 1994, p. 16.
- ↑ Rees 2005, pp. 96-97, 101.
- ↑ Testimony of Rudolf Hoess, Commandant of Auschwitz, University of Missouri-Kansas City School of Law; Hoess, Rudolf (1900-1947), camp commandant of Auschwitz, Yad Vashem. Retrieved December 22, 2009.
- ↑ Gustave Gilbert witness statement cited in Dwork and Van Pelt 2002, p. 278, cited in Rees 2005, p. 53.
- ↑ September 3: First experimental gassings at Auschwitz, Yad Vashem.
- ↑ Pressac: Auschwitz: Technique and Operation of the Gas Chambers Holocaust-History.org p. 100 reports that the timesheets of a civilian worker from the company building the crematorium furnaces prove that the installed ventilation system for removing the hydrocyan acid gas from Zyklon B application in the morgues worked well.
- ↑ Rees 2005, pp. 168-169.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 Dwork and van Pelt, 1997, p. 10.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 Gutman 1994, p. 17.
- ↑ Danuta Czech in Gutman 1994, p. 18.
- ↑ This image shows the arrival of Hungarian Jews from Carpatho-Ruthenia, many of them from the Berehov ghetto. The main entrance is visible in the background The Auschwitz Album, Yad Vashem.
- ↑ Rees 2005, p. 100.
- ↑ Rees 2005, pp. 172-175.
- ↑ Kárný 1994, p. 556.
- ↑ Dwork and van Pelt 1997, pp. 337-343.
- ↑ Gutman 1994, pp. 20-21.
- ↑ Gutman 1994, p. 21.
- ↑ Rees 2005, pp. 178-179.
- ↑ Rees 2005, pp. 180-182.
- ↑ Doctors from Hell: the Horrific Account of Nazi Experiments on Humans. By Vivien Spitz Publisher: Sentient Publications (May 25, 2005) ISBN 1-59181-032-9 ISBN 978-1-59181-032-2 Pages 232-234
- ↑ Substantive and Procedural Aspects of International Criminal Law : The Experience of International and National Courts: Materials by Gabrielle Kirk McDonald Publisher: Springer; 1 edition (March 1, 2000) ISBN 90-411-1134-4 ISBN 9789041111340
- ↑ Die Namen der Nummern (Gebundene Ausgabe) von Hans-Joachim Lang (Autor)Publisher: Hoffmann + Campe Vlg GmbH (August 31, 2004) ISBN 3-455-09464-3 ISBN 978-3-455-09464-0
- ↑ Garlinski 1975; IPN.gov.pl
- ↑ 38.0 38.1 38.2 Adam Cyra, Ochotnik do Auschwitz - Witold Pilecki 1901-1948, Oświęcim 2000. ISBN 83-912000-3-5
- ↑ Karny 1994, p. 556.
- ↑ Rees 2005, pp. 256-257.
- ↑ (English) Państwowe Muzeum Auschwitz-Birkenau w Oświęcimiu
- ↑ Rees 2005, pp. 141.
- ↑ Levi 1947.
- ↑ "Byłem Numerem: swiadectwa Z Auschwitz" by Kazimierz Piechowski, Eugenia Bozena Kodecka-Kaczynska, Michal Ziokowski, Hardcover, Wydawn. Siostr Loretanek, ISBN 83-7257-122-8
- ↑ "Auschwitz.org.pl". En.auschwitz.org.pl. 2009-01-13. http://en.auschwitz.org.pl/m/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=578&Itemid=8. Retrieved 2010-08-23.
- ↑ Daring to Resist: Jewish Defiance in the Holocaust Publisher: Museum of Jewish Heritage - A Living Memorial to the Holocaust (April 1, 2007) ISBN 0-9716859-2-4 ISBN 978-0-9716859-2-5
- ↑ The Holocaust: a history of the Jews of Europe during the Second World War By Martin Gilbert Pages 683-697; Publisher: Holt Paperbacks (May 15, 1987) ISBN 0-8050-0348-7 ISBN 978-0-8050-0348-2
- ↑ Rees 2005, pp. 260-265.
- ↑ Commandant of Auschwitz: Rudolf Höß. Appendix one, pp. 193-194. ISBN 1-84212-024-7
- ↑ Brian Harmon, John Drobnicki, Historical sources and the Auschwitz death toll estimates, The Nizkor Project
- ↑ 51.0 51.1 Nizkor, The Auschwitz Gambit: The Four Million Variant
- ↑ Wellers, Georges. Essai de determination du nombre de morts au camp d'Auschwitz (attempt to determine the number of dead at the Auschwitz camp), Le Monde Juif, Oct-Dec 1983, pp. 127-159.
- ↑ Piper 1994, pp. 68-72.
- ↑ Cesarani and Kavanaugh 2004, p. 357.
- ↑ Auschwitz by Debórah Dwork , Robert Jan van Pelt. page 166 Publisher: W. W. Norton & Company (April 17, 2002) ISBN 0-393-32291-2 ISBN 978-0-393-32291-0
- ↑ Beyond Justice: The Auschwitz Trial by Rebecca Wittmann Publisher: Harvard University Press (May 30, 2005) ISBN 0-674-01694-7 ISBN 978-0-674-01694-1
- ↑ Auschwitz, 1940-1945: Mass murder By Wacław Długoborski, Franciszek Piper
- ↑ Last Traces: The Lost Art of Auschwitz by Joseph Czarnecki Publisher: Macmillan Publishers ISBN 0-689-12022-2 ISBN 978-0-689-12022-0
- ↑ Auschwitz chronicle 1939-1945 By Danuta Czech Publisher: I B Tauris & Co Ltd (November 1990) ISBN 1-85043-291-0 ISBN 978-1-85043-291-3
- ↑ 60.0 60.1 Pressac, Jean-Claude and Van Pelt, Robert-Jan "The Machinery of Mass Murder at Auschwitz" in Gutman, Yisrael & Berenbaum, Michael. Anatomy of the Auschwitz Death Camp, Indiana University Press, 1994; this edition 1998, p. 232.
- ↑ 61.0 61.1 Pressac, Jean-Claude and Van Pelt, Robert-Jan "The Machinery of Mass Murder at Auschwitz" in Gutman, Yisrael & Berenbaum, Michael. Anatomy of the Auschwitz Death Camp, Indiana University Press, 1994; this edition 1998, p. 234.
- ↑ Morris, Errol. "Mr. Death: Transcript". http://www.errolmorris.com/film/mrd_transcript.html. Retrieved May 15, 2008.
- ↑ The Twentieth Train: The True Story of the Ambush of the Death Train to Auschwitz by Marion Schreiber Publisher: Grove Press (February 5, 2004) ISBN 0-8021-1766-X ISBN 978-0-8021-1766-3
- ↑ Children of the Flames; Dr. Josef Mengele and the Untold Story of the Twins of Auschwitz by Lucette Matalon and Sheila Cohen Dekel Publisher: Penguin (Non-Classics) (May 1, 1992) ISBN 0-14-016931-8 ISBN978-0140169317
- ↑ Pressac, Jean-Claude and Van Pelt, Robert-Jan "The Machinery of Mass Murder at Auschwitz" in Gutman, Yisrael & Berenbaum, Michael. Anatomy of the Auschwitz Death Camp, Indiana University Press, 1994; this edition 1998, p. 236.
- ↑ From the history of KL-Auschwitz, Volume 1 - Page 73 Kazimierz Smoleń - History - 1967
- ↑ Testimony from the Nazi camps: French women's voices By Margaret-Anne Hutton pages 34-36Publisher: Routledge; 1 edition (December 29, 2004) ISBN- 0415349338 ISBN 978-0-415-34933-8
- ↑ Rena's Promise By Rena Kornreich Gelissen, Heather Dune Macadam pages 230-34Publisher: Beacon Press (October 30, 1996) ISBN 0-8070-7071-8 ISBN 978-0-8070-7071-0
- ↑ Müller, Melissa. Anne Frank: The Biography Macmillan, 1998. ISBN 0-8050-5996-2 pp. 119–120
- ↑ Karny, Miroslav. "The Vrba and Wetzler Report" in Gutman, Yisrael & Berenbaum, Michael. Anatomy of the Auschwitz Death Camp, Indiana University Press, 1994; this edition 1998, pp. 563–564.
- ↑ The Murders at Bullenhuser Damm: The SS Doctor and the Children Günther Schwarberg Publisher: Indiana University Press; First Edition edition (April 1984) ISBN 0-253-15481-2 ISBN 978-0-253-15481-1
- ↑ "Auschwitz.org.pl". En.auschwitz.org.pl. http://en.auschwitz.org.pl/m/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=227&Itemid=13&limit=1&limitstart=1. Retrieved 2010-08-23.
- ↑ Oliver Lustig. "Concentration Camp Dictionary "F-G"]". Isurvived.org. http://isurvived.org/Lustig_Oliver-CCDictionary/CCD-05_FG.html#B5. Retrieved 2010-08-23.
- ↑ "Auschwitz death camp sign stolen". BBC News. December 18, 2009. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/europe/8419948.stm. Retrieved December 18, 2009.
- ↑ Connolly, Kate. Poland declares state of emergency after 'Arbeit Macht Frei' stolen from Auschwitz, The Guardian, December 18, 2009.
- ↑ Poland: Foreigner Is Suspected in Theft of Auschwitz Sign, Associated Press, December 22, 2009.
- ↑ News.Yahoo.com
- ↑ Police in Poland find sign stolen from Auschwitz gate, BBC News, December 21, 2009.
- ↑ SLtrib.com
- ↑ Gera, Vanessa (December 21, 2009). "Damaged Auschwitz sign to go back up at main gate". The Associated Press. The Salt Lake Tribune. http://www.sltrib.com/ci_14044451. Retrieved December 23, 2009.
- ↑ "Telegraph.co.uk". Telegraph.co.uk. 2009-12-21. http://www.telegraph.co.uk/news/worldnews/europe/poland/6854075/Auschwitz-sign-found-in-three-pieces.html. Retrieved 2010-08-23.
- ↑ Fish, Sandra. "Politicsdaily.com". Politicsdaily.com. http://www.politicsdaily.com/2010/01/01/auschwitz-sign-theft-linked-to-far-right-terrorist-plot/. Retrieved 2010-08-23.
- ↑ "DigitalJournal.com". DigitalJournal.com. http://www.digitaljournal.com/article/284804. Retrieved 2010-08-23.
- ↑ "Aftonbladet.se". Aftonbladet.se. 2010-03-11. http://www.aftonbladet.se/nyheter/article6760745.ab. Retrieved 2010-08-23.
- ↑ Daily Telegraph, page 20, issue of Friday 19 March 2010.
- ↑ Associated, The. "Auschwitz sign thieves fail to show up for prison terms - Haaretz Daily Newspaper | Israel News". Haaretz.com. http://www.haaretz.com/jewish-world/news/auschwitz-sign-thieves-fail-to-show-up-for-prison-terms-1.284630. Retrieved 2010-05-18.
- ↑ Associated, The (2010-04-21). "Auschwitz Thieves Fail to Report to Jail". NYTimes.com. http://www.nytimes.com/2010/04/22/world/europe/22poland.html. Retrieved 2010-05-18.
- ↑ "Men jailed for stealing Auschwitz camp sign failed to return after compassionate leave". mirror.co.uk. http://www.mirror.co.uk/news/top-stories/2010/04/22/auschwitz-thieves-flee-115875-22203083/. Retrieved 2010-05-18.
- ↑ Five killed and thousands evacuated as floods hit central Europe - Telegraph
References
- Cesarani, David and Kavanaugh, Sarah (2004). Holocaust: Critical Concepts in Historical Studies. Routledge. ISBN 0-415-27512-1, 9780415275125
- Czech, Danuta (ed.) (1989). Kalendarium der Ereignisse im Konzentrationslager Auschwitz-Birkenau 1939–1945, Reinbek bei Hamburg.
- Dawidowicz, Lucy (1979). The War Against the Jews. New York: Bantam Books.
- Dwork, Deborah and Robert Jan van Pelt. Auschwitz: 1270 to the Present. 1997, Norton Paperback edition, ISBN 0-393-31684-X
- Garlinski, Josef (1975). Fighting Auschwitz: the Resistance Movement in the Concentration Camp. Fawcett. ISBN 0-449-22599-2
- Gutman, Yisrael and Berenbaum, Michael (eds.) (1998). Anatomy of the Auschwitz Death Camp. Indiana University Press; first published 1994.
- Hilberg, Raul (1961). The Destruction of the European Jews. Chicago: Quadrangle Books.
- Levi, Primo (1947). If This Is a Man. First published in Italy in 1947, first translated into English 1958.
- Kárný, Miroslav (1994). "The Vrba and Wetzler report," in Gutman and Berenbaum, 1998.
- Krakowski, Shmuel (1994). "The Satellite Camps" in Gutman and Berenbaum, 1998.
- Piper, Franciszek (1994). "The Number of Victims" in Gutman and Berenbaum, 1998.
- Rees, Laurence (2005). Auschwitz: A New History. Public Affairs, 2005. ISBN 1-58648-303-X
- Rees, Laurence (2009). Rudolf Höss - Commandant of Auschwitz, BBC, November 5, 2009.
- Wittmann, Rebecca Elizabeth. "Indicting Auschwitz? The Paradox of the Frankfurt Auschwitz Trial," German History, volume 21, issue 4, Oxford University Press, October 2003, doi 10.1191/0266355403gh294oa
Further reading
- Memorial and museum website
- Boyne, John (2006). The Boy in the Striped Pyjamas Great Britain: David Fickling Books, 2006 ISBN 0-385-75106-0
- Cyra, Adam (2000). Ochotnik do Auschwitz - Witold Pilecki 1901-1948, Oświęcim 2000. ISBN 83-912000-3-5
- Dlugoborski, Waclaw, and Franciszek Piper (eds.) (2000). Auschwitz, 1940-1945: Central Issues in the History of the Camp Five Vols. Oświęcim: Auschwitz-Birkenau State Museum. ISBN 83-85047-87-5
- Gilbert, Martin (1981). Auschwitz and the Allies New York: Holt, Rinehart and Winston, 1981 Photographs, maps. ISBN 0-03-057058-1
- Muller, Filip Eyewitness Auschwitz: Three Years in the Gas Chambers Ivan R Dee Inc, 1999 ISBN 1-56663-271-4
- Nyisli, Miklos Auschwitz: A Doctor's Eye-witness Account Mayflower, 1977 ASIN B000QIZILC
- van Pelt, Robert Jan. The Case for Auschwitz: Evidence from the Irving Trial. Indiana University Press, 2002. ISBN 0-253-34016-0
- Druhasvetovavalka.cz, - Pages show pictures and videos of the day taken at places connected with the World War II
- Auschwitz-Birkenau Memorial and Museum (English), (Georgian), (Polish) – Official website
- A Virtual Tour of Auschwitz/Birkenau Annotated images of the camp (accessed 02/14/08)
- Interactive image map of Birkenau
- Auschwitz Jewish Center situated in the town of Oświęcim
- (Polish) Auschwitz-Birkenau and city Oswiecim
- Data and summary facts
- Video footage from a 2003 visit to Auschwitz-Birkenau
- Selected Photos from the Auschwitz Album with commentary by Oliver Lustig
- Liberation of Auschwitz - 60th Anniversary United States Holocaust Memorial Museum
- Holocaust Encyclopedia - Auschwitz United States Holocaust Memorial Museum
- Cybrary of the Holocaust Holocaust education site
- Anna Heilman Anna Heilman is the last living survivor of the plot to blow up Crematorium IV at Auschwitz-Birkenau. Her Holocaust experiences are discussed in her novel Never Far Away: The Auschwitz Chronicle of Anna Heilman
- Auschwitz-Birkenau 2005 Photographs and commentary marking the 60th anniversary of the camp's liberation
- Photos From Auschwitz and Birkenau Detailed Photos From Auschwitz and Birkenau by Alan Jacobs
- Virtual Reality panoramas of Auschwitz and Birkenau Interactive Virtual Reality panoramas of Auschwitz and Birkenau
- Auschwitz, Then and Now Photo/Art Exhibit Paintings by survivor Jan Komski – click and see an actual photo taken in the same place depicted in the painting
- Auschwitz: The Nazis and the 'Final Solution', BBC.
- The Simon Wiesenthal Center
- Auschwitz and Birkenau at Google Maps
- CBC Digital Archives - Life after Auschwitz
External links
- Escape From Auschwitz
- Auschwitz Memorial
- The Auschwitz Album - Online exhibition from Yad Vashem
- The Auschwitz-Birkenau Blueprints- Architecture of Murder - Online exhibition from Yad Vashem
|
|||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||